MIMIC SYSLOG Protocol Module Guide
-
Table of Contents
-
Overview
-
Installation
SYSLOG support is made available in MIMIC as an optional dynamically loadable module. Starting with MIMIC 10.00, you can use the Protocol Wizard to install the SYSLOG module. If you prefer to enable SYSLOG by hand, you need to do the following:
-
Use File->Terminate to stop the any running MIMIC daemon.
-
Copy the SYSLOG shared library (syslog.dll on Windows, syslog.so on Unix)
from "bin/dynamic/optional" to "bin/dynamic" in the
install directory.
-
Restart MIMIC.
You should see the following type of message in the MIMICLog that
confirms that the SYSLOG module was properly loaded :
INFO - SYSLOG : Loaded protocol from < path-to-DLL > INFO - SYSLOG v7.00
Once SYSLOG is loaded, any agent instance configured to support the SYSLOG protocol will be able to send SYSLOG events to a SYSLOG server.
-
Use File->Terminate to stop the any running MIMIC daemon.
-
Using SYSLOG from MIMICView
If the SYSLOG module is enabled, then Agent->Add, Agent->Configure and Agent->Paste dialogs will display SYSLOG as an additional checkbox in the Advanced pane along with the SNMP protocols. On selecting the checkbox a new SYSLOG pane will appear.
This SYSLOG configuration pane lets the user configure the parameters for a SYSLOG session:
-
Server
This optional parameter specifies the SYSLOG server(s) remote IP address (not localhost) to send messages to. If more than one, they need to be space separated. The default is no server, causing no SYSLOG messages to be generated.
-
Server Port
This optional parameter specifies the SYSLOG server well-known port. The default is the standard port 514.
-
Local Port
This mandatory parameter specifies the local port to use. The default is 0, which means to auto-assign a port number.
The remaining configurables are ignored and need to be set with the mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set attr command below.
-
Server
-
Using SYSLOG from MIMICShell
A few new commands and some enhanced old commands can be used from the MIMICShell to control the SYSLOG functionality. Here is a synopsis:
-
mimic protocol msg SYSLOG get args
This command lets the user gather the self-defining list of arguments required and their particulars. The parameters are detailed above. A sample exchange for this command would be:
mimicsh> mimic protocol msg SYSLOG get args {{server} {Server} {string} {} {optional} {}} {{serverport} {Server Port} {string} {} {optional} {514}} {{client} {Client} {string} {} {optional} {}} {{localport} {Local Port} {integer} {} {optional} {}} {{sequence} {Sequence} {integer} {} {optional} {}} {{separator} {Separator} {string} {} {optional} {}} {{timestamp} {Timestamp} {string} {} {optional} {}} {{hostname} {Hostname} {string} {} {optional} {}} -
mimic agent get protocol
This command lets the user look at the protocols currently configured on the agent. A sample exchange for this command would be:
mimicsh> mimic agent get protocol snmpv1,snmpv2c,SYSLOG
-
mimic agent set protocol
This command lets the user change the protocol setting for an agent. A sample exchange for this command would be:
mimicsh> mimic agent get protocol snmpv1 mimicsh> mimic agent set protocol snmpv1,SYSLOG mimicsh> mimic agent get protocol snmpv1,SYSLOG
-
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG state
This command lets the user query the state of the SYSLOG agent. This is particularly useful at agent startup time to wait for SYSLOG startup. A sample usage for this command would be:
if { [mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG state] != "up" } { # do necessary to wait until SYSLOG is up } -
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get config
This command lets the user get the current argument settings. A sample exchange for this command would be:
mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get config {server=} {serverport=514} {client=} {localport=0} {sequence=} {separator=} {timestamp=} {hostname=} -
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set config [config]
This command lets the user change the current argument settings of all SYSLOG sessions for an agent. A sample exchange for this command would be:
mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get config {server=} {serverport=514} {client=} {localport=0} {sequence=} {separator=} {timestamp=} {hostname=} mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set config localport=514 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get config {serverport=514} {localport=514} -
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get trace
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set trace [0 or 1]This command lets the user change the SYSLOG tracing configuration for an agent. A sample exchange would be:
mimicsh> mimic agent assign 9 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get trace 0 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set trace 1 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get trace 1
and the log would show:INFO - agent 9 trace enabled for SYSLOG INFO - agent 9 configured at 10.0.0.9,161. INFO - agent 9 loading INFO - agent 9 loaded device Agent 9 invoking start+syslog.mtcl INFO - SYSLOG[AGT=9]: sent to [192.9.200.71,514] - <3>Oct 01 11:23:41 cisco-7513 Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software IOS (tm) RSP Software (RSP-JSV56I-M), Version 12.1(7), RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Copyright (c) 1986-2001 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Fri 23-Feb-01 05:14 by kellythw
-
mimic protocol msg SYSLOG get stats_hdr
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get statisticsReturns SYSLOG statistics information:
- a list of statistic headers, and
- current statistics values for the specified client.
In order, the statistic values are:
- Total number of SYSLOG packets sent.
- Total number of SYSLOG packets discarded.
A sample exchange for these commands would be:
mimicsh> mimic protocol msg SYSLOG get stats_hdr {{pktSnt} {PktsSent}} {{pktDisc} {PktsDiscarded}} mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get statistics 1 0 -
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send pri msg
This command sends a SYSLOG event to the server(s) with the specified PRI and MSG fields. It can only be used after starting the agent.
By default, the format of the message will adhere to the standard RFC 3164. The standard format of the message is
>PRI<[>SEQ<>SEP<]>TIMESTAMP<>SEP<[>HOSTNAME<>SEP<]>MSG<
where fields between [] are optional, and between >< are substituted as follows:
- PRI is the PRI field of RFC 3164
- SEQ is an optional sequence number (used by Cisco IOS)
- SEP is a separator, " " by default
- TIMESTAMP is the TIMESTAMP field of RFC 3164
- HOSTNAME is the HOSTNAME field of RFC 3164
- MSG is the MSG field of RFC 3164
However, this can be modified with the following commands.
- PRI is the PRI field of RFC 3164
-
mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set attr value
where attr is one of the following:
- server - a space-separated list of server,port
- client - the source address for messages. Must be one of the IP aliases of this agent
- sequence - the starting sequence number, if any. By default, none.
- separator - the separator in the HEADER field, by default a space
- timestamp - either "clock" (default) for real-time clock, "sysUpTime" for timestamp based on the value of sysUpTime.0, or any other string.
- hostname - the hostname, by default the value of sysName.0
to control the above fields. A sample exchange for these commands would be (eg. to create an identical message to that of Cisco IOS):
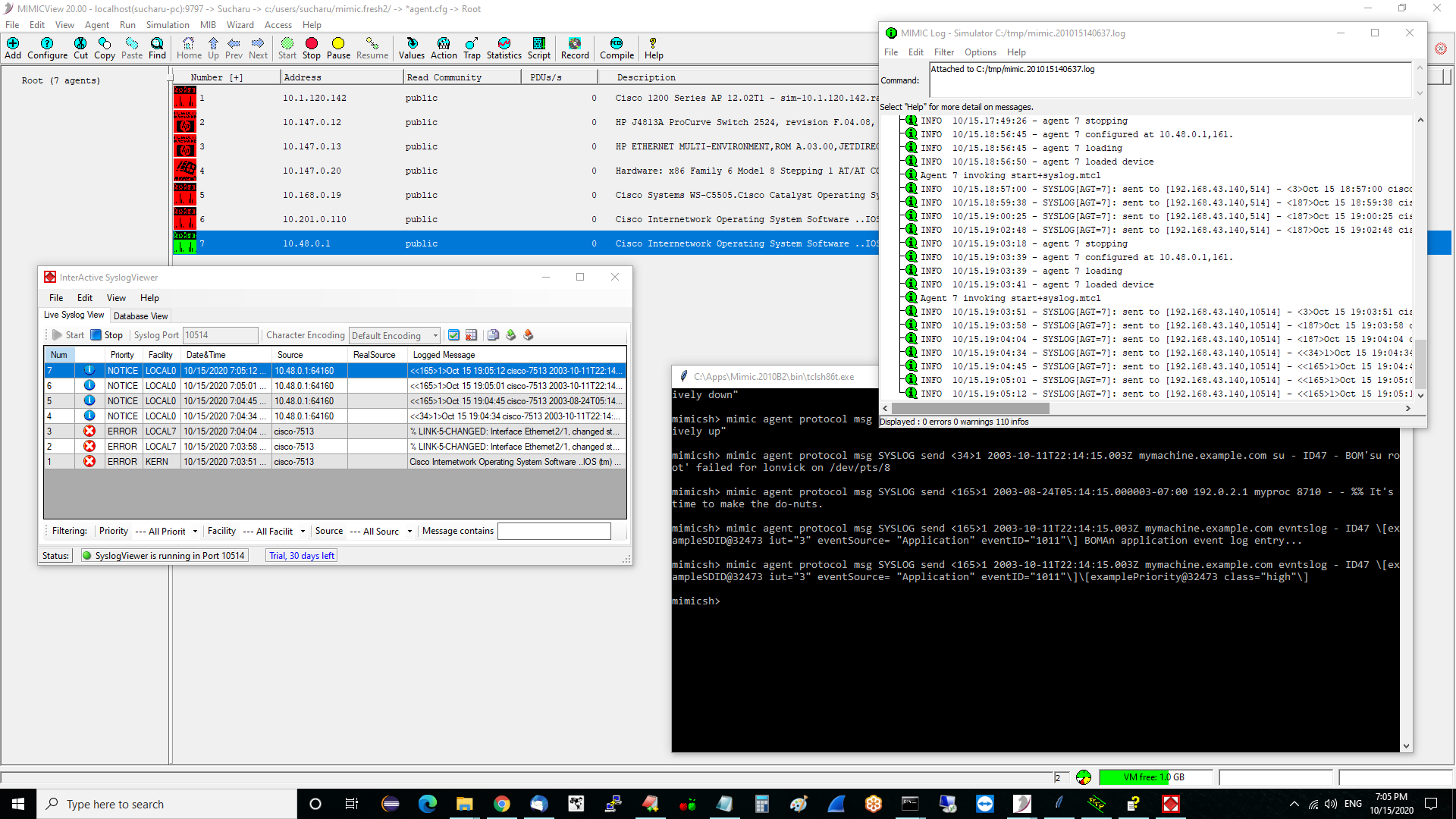
mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set server \{192.9.200.70 192.9.200.84\} mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get server 192.9.200.70,514 192.9.200.84,514 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set sequence 32 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set separator \{: \} mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set hostname \{\} mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG set timestamp sysUpTime mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send 189 %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by vty0 (192.9.200.76) mimicsh> mimic protocol msg SYSLOG get stats_hdr {{pktSnt} {PktsSent}} {{pktDisc} {PktsDiscarded}} mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get statistics 1 0 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send 187 "% LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface Ethernet2/1, changed state to administratively down" mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG get statistics 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0These commands generate the example messages in RFC 5424 section 6.5:mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send <34>1 2003-10-11T22:14:15.003Z mymachine.example.com su - ID47 - BOM'su root' failed for lonvick on /dev/pts/8 mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send <165>1 2003-08-24T05:14:15.000003-07:00 192.0.2.1 myproc 8710 - - %% It's time to make the do-nuts. mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send <165>1 2003-10-11T22:14:15.003Z mymachine.example.com evntslog - ID47 \[exampleSDID@32473 iut="3" eventSource= "Application" eventID="1011"\] BOMAn application event log entry... mimicsh> mimic agent protocol msg SYSLOG send <165>1 2003-10-11T22:14:15.003Z mymachine.example.com evntslog - ID47 \[exampleSDID@32473 iut="3" eventSource= "Application" eventID="1011"\]\[examplePriority@32473 class="high"\]
and this shows in the log if tracing is enabled:
INFO 10/15.17:15:43 - SYSLOG[AGT=7]: sent to [192.168.43.140,514] - <<34>1>Oct 15 17:15:43 cisco-7513 2003-10-11T22:14:15.003Z mymachine.example.com su - ID47 - BOM'su root' failed for lonvick on /dev/pts/8 INFO 10/15.17:18:20 - SYSLOG[AGT=7]: sent to [192.168.43.140,514] - <<165>1>Oct 15 17:18:20 cisco-7513 2003-08-24T05:14:15.000003-07:00 192.0.2.1 myproc 8710 - - %% It's time to make the do-nuts. INFO 10/15.17:19:47 - SYSLOG[AGT=7]: sent to [192.168.43.140,514] - <<165>1>Oct 15 17:19:47 cisco-7513 2003-10-11T22:14:15.003Z mymachine.example.com evntslog - ID47 [exampleSDID@32473 iut="3" eventSource= Application eventID="1011"] BOMAn application event log entry... INFO 10/15.17:20:29 - SYSLOG[AGT=7]: sent to [192.168.43.140,514] - <<165>1>Oct 15 17:20:29 cisco-7513 2003-10-11T22:14:15.003Z mymachine.example.com evntslog - ID47 [exampleSDID@32473 iut="3" eventSource= Application eventID="1011"][examplePriority@32473 class="high"]
-
mimic protocol msg SYSLOG get args
-
Compatibility
The Unix syslog servers work out of the box with the MIMIC SYSLOG module, provided that the syslog server is setup to receive network messages.
This section details further interoperability with some widely available Windows syslog servers.
Tftpd32
Download Url Version Size http://tftpd32.jounin.net/ 2.80 173 KB Installation and usage
- Extract the tftpd32.280.zip file.
- Run tftpd32.exe from the Extracted Location.
- Click settings, Change the base directory to a location of your choice.
- Check enable the "Save syslog messages" if you wish to save the syslog messages to a file.
- Click Ok, to confirm changes.
- Click "Syslog server" tab.
Uninstallation
- Execute the uninst.exe file.
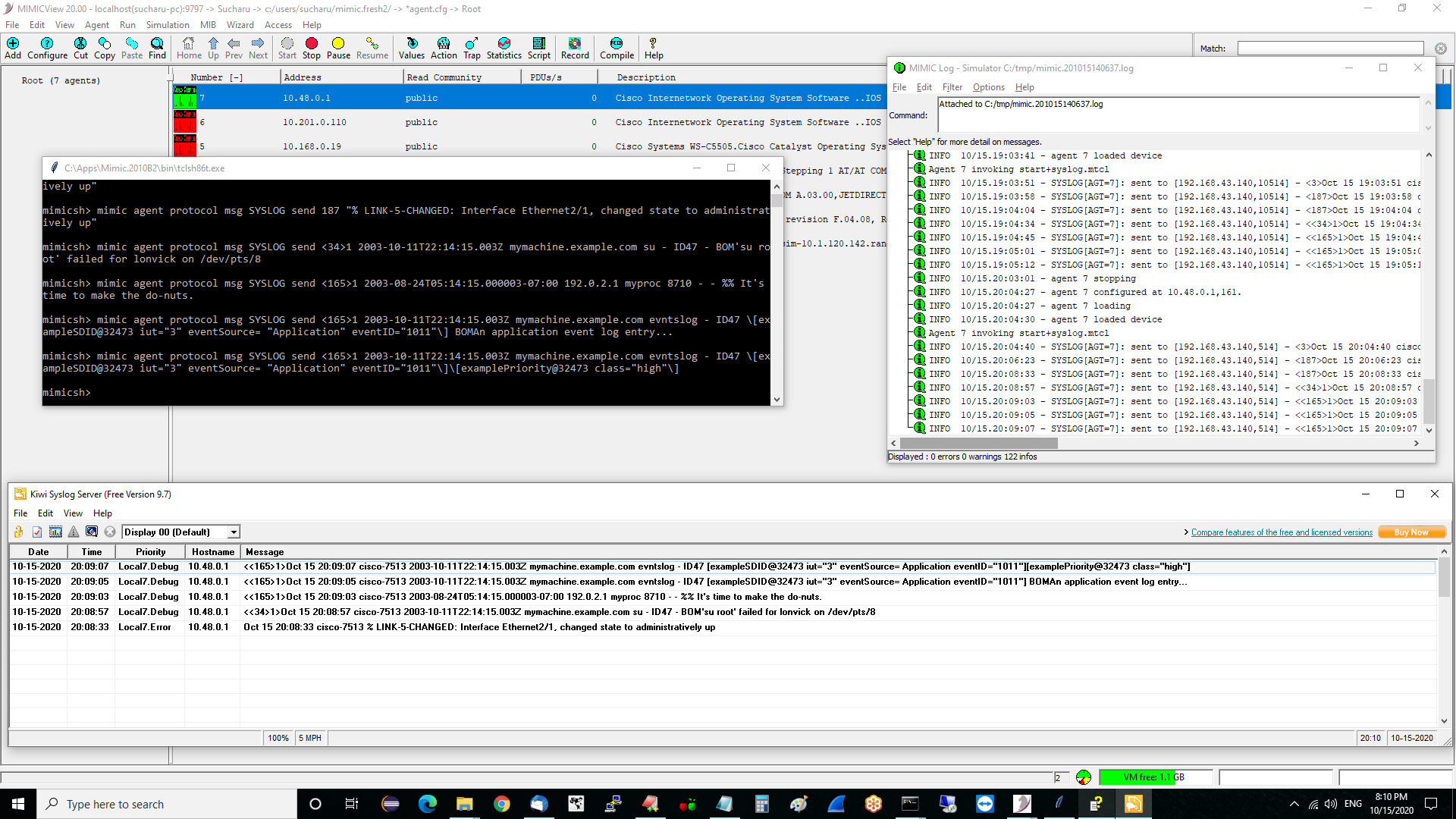
Kiwi Syslog
Download Url Version Size http://www.kiwisyslog.com/ 9.7 4.56 MB Kiwi Syslog daemon comes in two versions : Standard Version and Service Version. The Kiwi_Syslogd.exe i.e. Standard version runs as a daemon while Kiwi_Syslogd_Service.exe i.e. Service version can be installed to run the application as a windows service.
Installation and usage
- To install the Kiwi Syslog execute the Kiwi_Syslogd.exe Or Kiwi_Syslogd_Service.exe.
- Kiwi can now log messages, but if you wish to configure advanced options follow steps 2 through 5 else you can continue with instruction for Vlab.
- To Change the files location where syslog messages will be saved, click File->Setup.
- Specify whether you want the messages to be saved to file under the Rules->Default->Action Tree.
- You can also specify TCP, UDP, SNMP logging under the inputs tree.
- Press Ok to confirm changes.
Uninstallation
- In the Control Panel->Add Remove Programs
- Select Kiwi Syslog Deamon->press Remove
- Follow instructions if any to remove the program
WinSyslog
Download Url Version Size https://www.winsyslog.com/download/ 16.2b 10.7 MB
Installation and usage
- To install the WinSyslog execute the wnsyslog.exe and follow the instructions.
- Execute the WINSyslogClient.exe client application from the location where you have installed it.
- Execute the interactive syslog server (InteractiveSyslogServer.exe)
- Click the start logging button to log syslog messages.
Uninstallation
- In the Control Panel->Add Remove Programs
- Select WinSysLog->press Remove
- Follow instructions if any to remove the program