MIMIC NETFLOW Module Compatibility
The MIMIC NETFLOW Protocol Module is an optional facility that simulates Cisco NetFlow exporters. This section details interoperability of MIMIC NETFLOW with third-party NetFlow collector and analysis applications.
-
Table of Contents
-
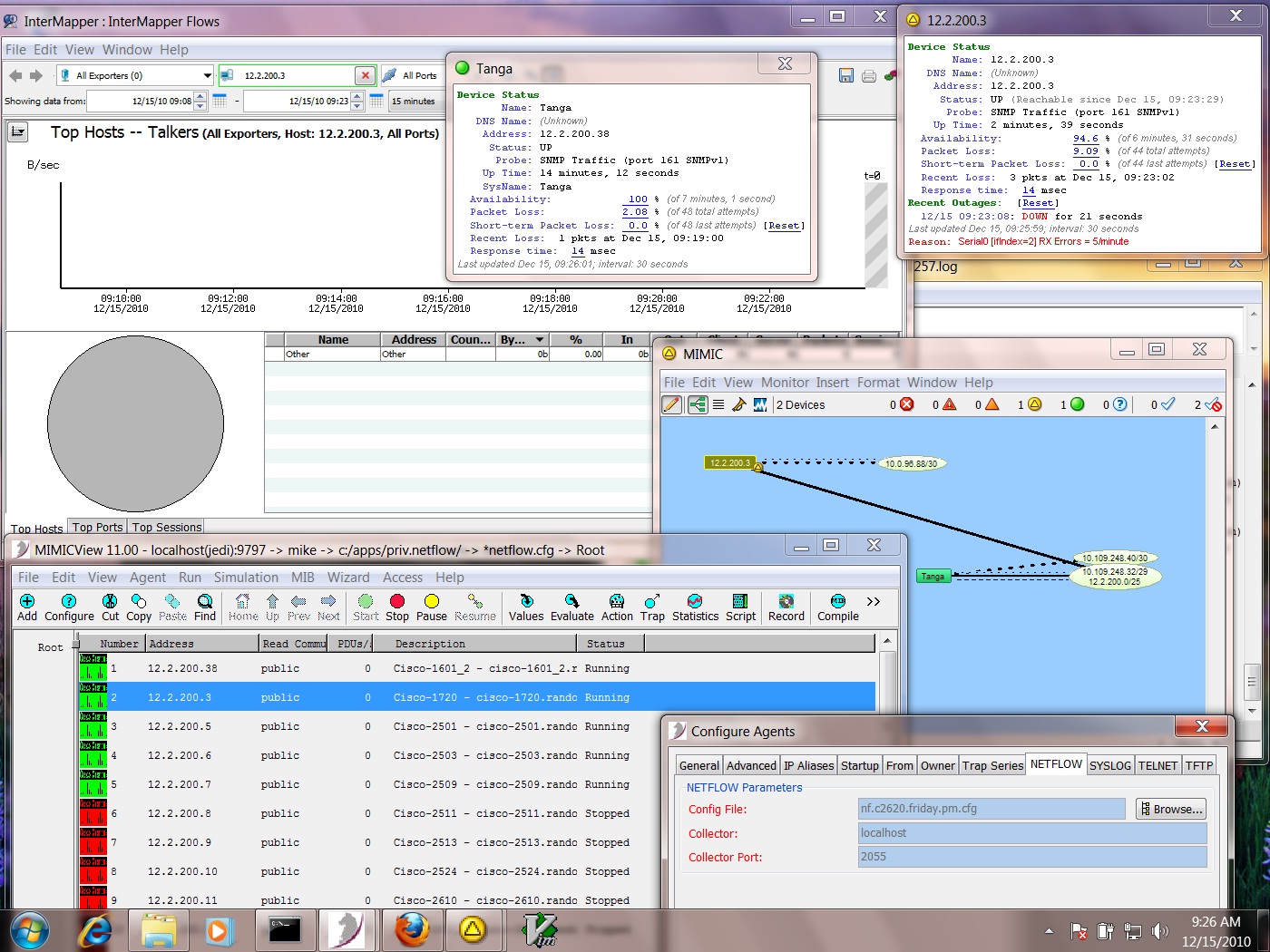
Example: InterMapper Flows
To use InterMapper Flows, download and install InterMapper from the product site. Also download the optional netflow module, InterMapper Flows and install it. Test licenses are available via email.
By default, InterMapper checks port 2055 for incoming NetFlow packets. Configure the MIMIC agent to export to the system that InterMapper is installed on with port 2055 specified. Select a NetFlow configuration file for the agent and start the agent.
In InterMapper, start a new map and add a device to it with the IP address of the MIMIC agent. If IP connectivity is possible, the device should be discovered and added to the map in InterMapper. Right-click on the new device and choose Flows Window from the context menu. An InterMapper Flows window will open showing collected flow data.
-
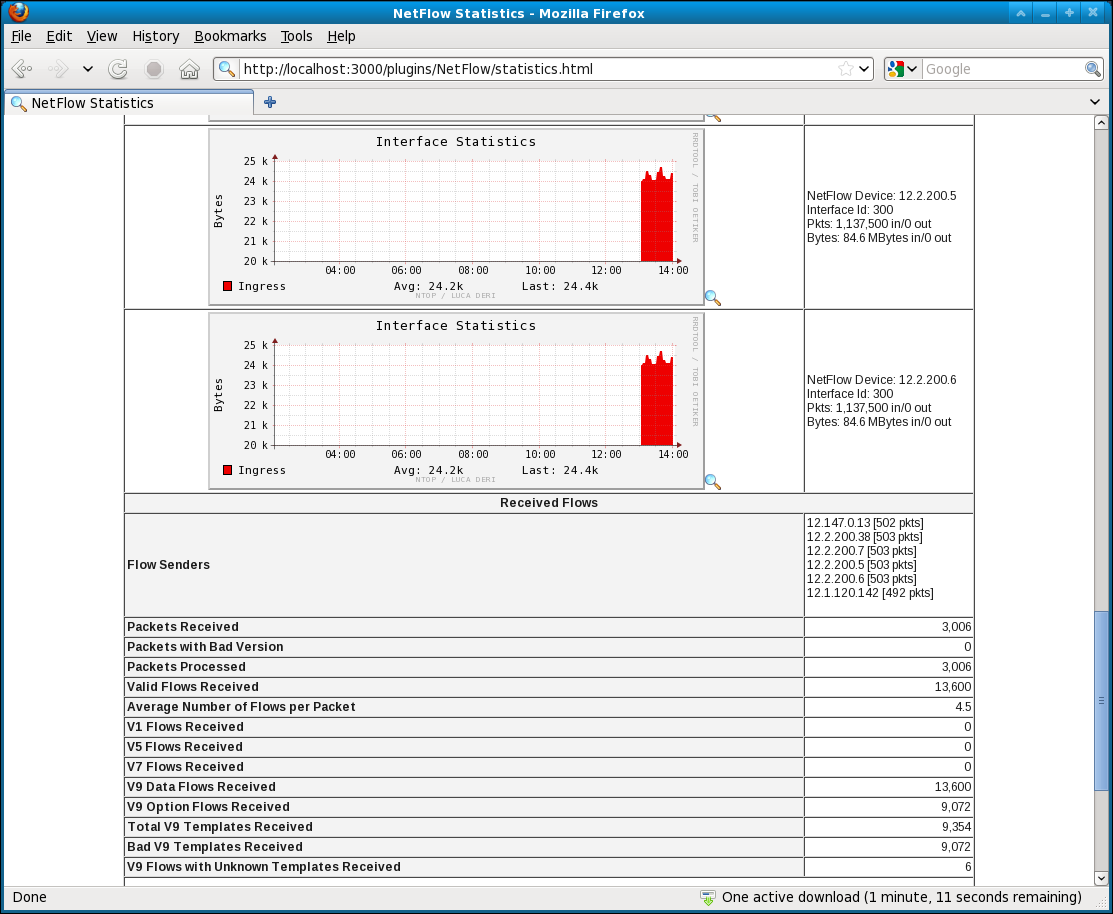
Example: NTOP
To use ntop, download and install it from the product site. Linux and Solaris users may also need to install rrdtool, which is a prerequisite for ntop.
Once ntop has been successfully installed and started, it may be accessed in a web browser pointing to port 3000 on the ntop host. Configuration of netflow collection is started by activating the netflow plugin under the plugins menu in the browser window. Use admin as the login to perform configuration.
In MIMIC, configure an agent with a netflow configuration file, set the ntop host system as Collector and specify a port to receive the exported flow data. Port 9999 is the default, but this is configurable in the netflow configuration tool in ntop. using the Admin->Configure->Preferences dialog.
-
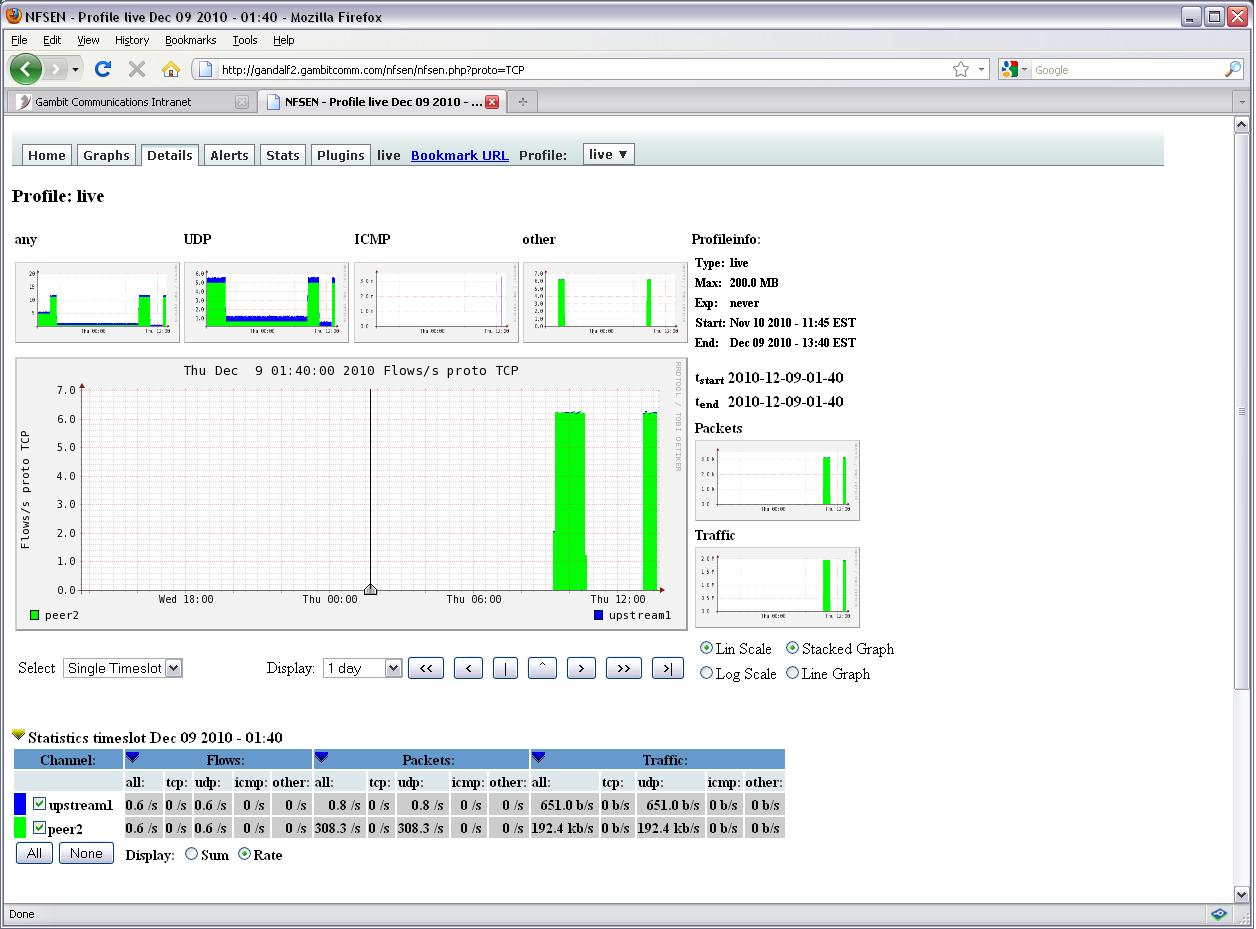
Example: NfSen
To use NfSen, download and install it from the download site. Note the prerequisites include nfdump and rrdtool, and the tool is not suppported on Windows.
When configuring NfSen for initial startup, the user configures netflow collection and other parameters in the file nfsen.conf in the %sources section. Careful attention to usernames and file protections will help the process, and it is suggested that new users look for guidance in user forums on the Web.
Once NfSen has been configured, started, and is accessible from a web browser, configure MIMIC agents for netflow using an appropriate netflow configuration file, listing the NfSen host in the Collector field, and specifying a port number as configured on the NfSen host. Once the agent has been sending flows for a couple of 5-minute collection periods, you should see data in the NfSen graphs. It may be necessary to refresh the browser page or explore the tabs on the NfSen page at first.
-
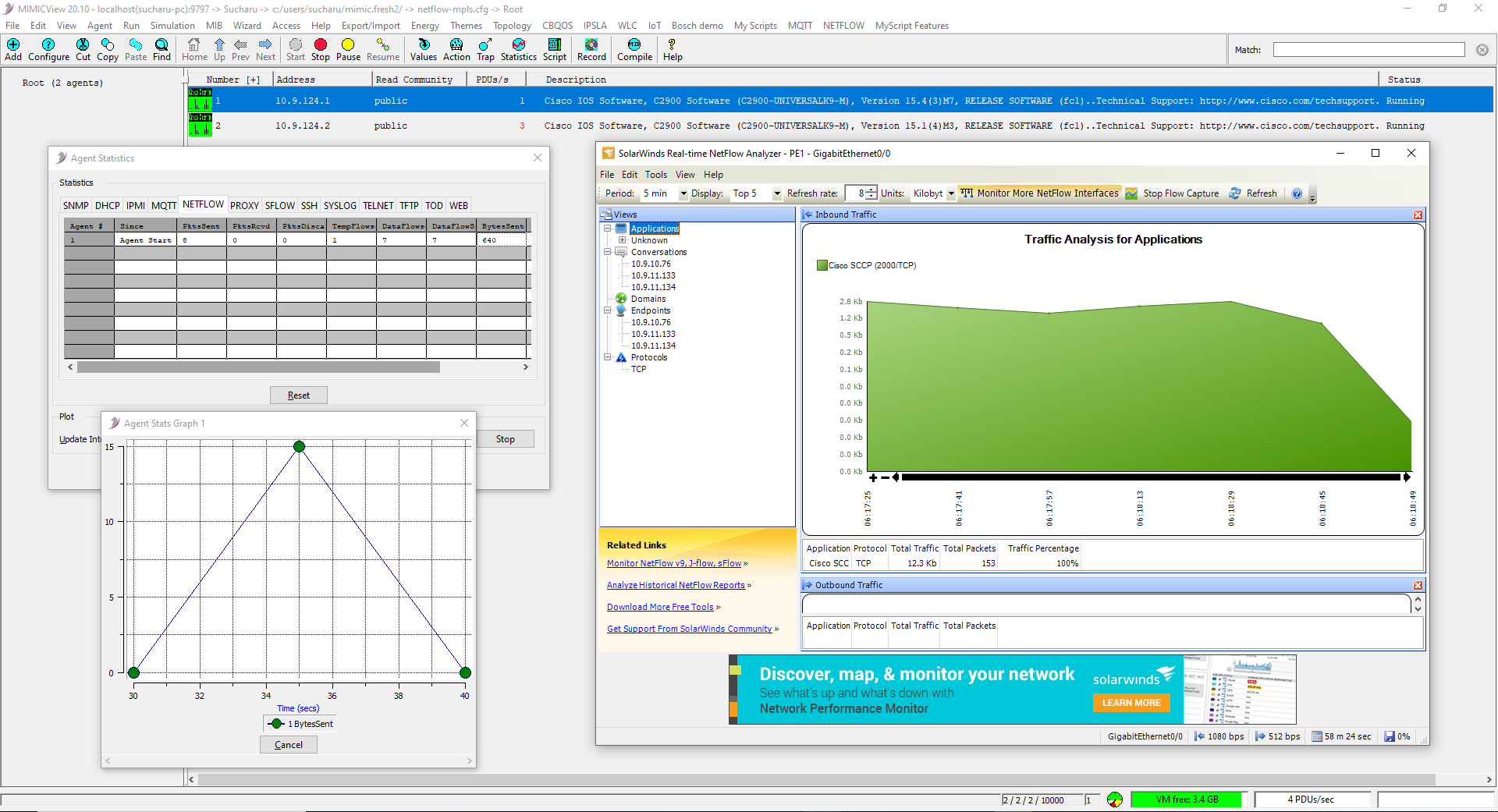
Example: Solarwinds
-
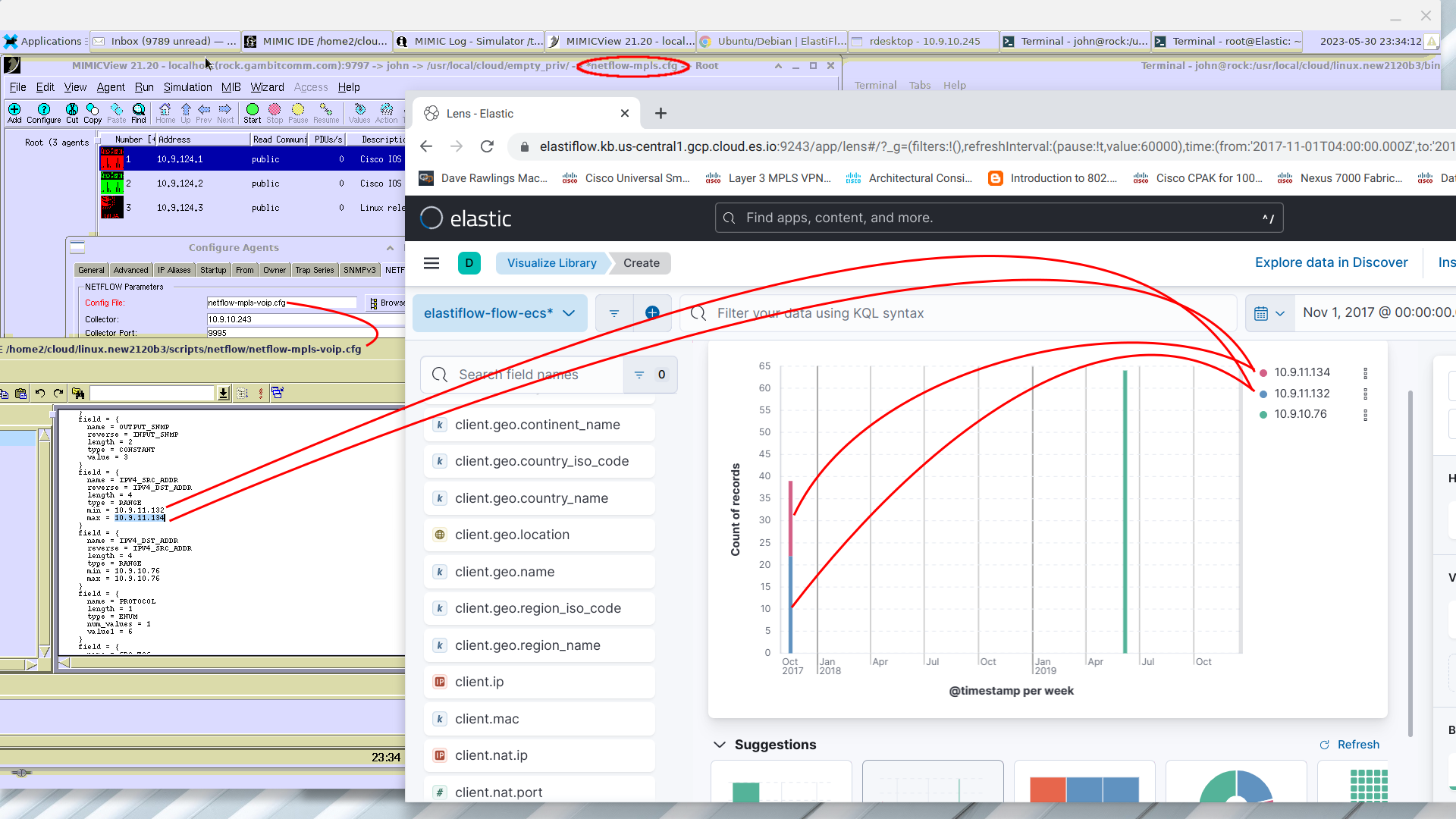
Example: ElastiFlow
-
Example Video: Scrutinizer
-
Example Video: Intermapper
-
Example Video: OpenObserve
-
Example: NBAR
Our advanced NBAR simulation was tested with multiple applications (Scrutinizer, Solarwinds, Sevone).